From luxury shopping to breathtaking architecture and rich cultural treasures, experience the best things to do in Jakarta with our travel guide.
READ MORE
Alice x Apéritif Restaurant, Bali
Experience a two-day collaboration between Apéritif Restaurant, Bali and Alice, curated by Chef Nic Vanderbeeken. Indulge in a special menu, complemented by expertly crafted cocktails from Panji Wisrawan, Head Mixologist of Pinstripe Bar (World's Top 500 Bars).
Don't miss an exlusive bar takeover by Panji Wisrawan at Artesian Rooftop Bar on Saturday, 12 April 2025.
DATE
11 - 12 April 2025
CONTACT US
For further information, contact us through WhatsApp at +62 858-8388-8881

An exclusive culinary experience presented by Chef Nic Vanderbeeken of Apéritif Restaurant, Bali, winner of Travel + Leisure's Tastemakers 2024.
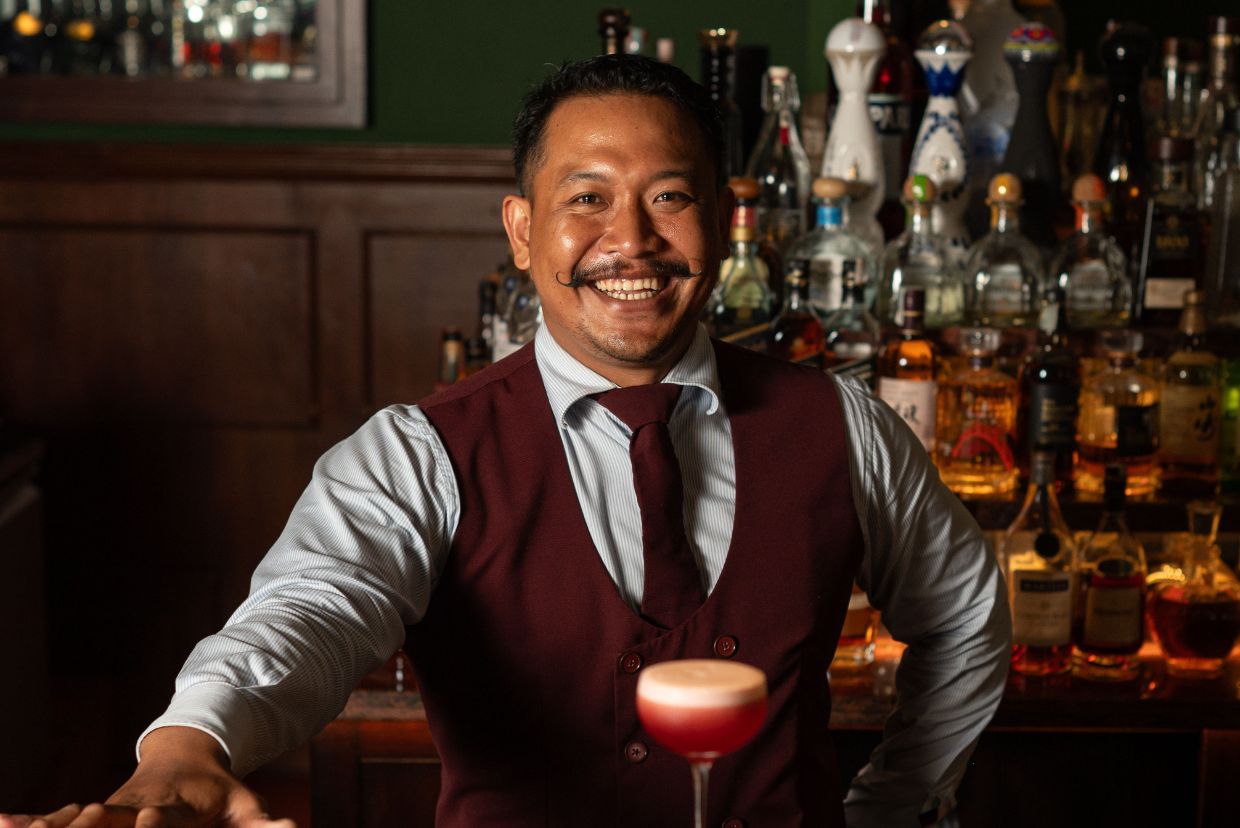


Join us for a Bar Takeover with expertly crafted cocktails by the award-winning bartender Panji Wisrawan, Head Mixologist of Pinstripe Bar, Bali (World's Top 500 Bars)
11 April at Alice
12 April at Artesian





